Contact: Bruce
Tel: +86-755-22 666 190
Fax: +86-755-29 043 136
E-mail: sales@ultrasonic-sensors.net
Skype: longsunac
Address: Room A1, 6/F, Bldg. No. 531, Bagua 3rd Road No. 277, Futian District, Shenzhen, China 518029
1. Application theory
Piezoelectric effect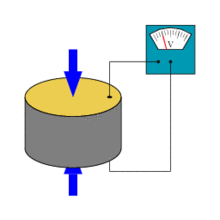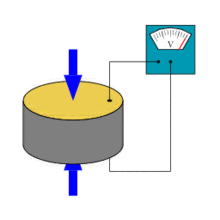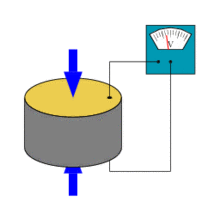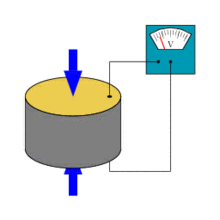
The piezoelectric effect describes the relation between a mechanical stress and an electrical voltage in solids. It is reversible: an applied mechanical stress will generate a voltage and an applied voltage will change the shape of the solid by a small amont (up to 4% change in volume). In physics, the piezoelectric effect can be described as the link between electrostatics and mechanics
(A piezoelectric disk generates a voltage when deformed (change in shape is greatly exaggerated, pictures shown on the right from wikipedia)
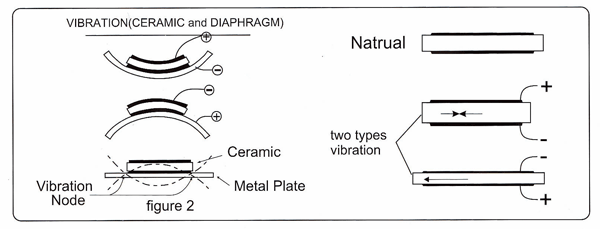
The ultrasonic sensor application theory
When an AC voltage drives the piezoelectric ceramic, it mechanically vibrates with a certain frequency. The opposition is true, when the ceramic vibrates, it will produce an AC voltage. This is the piezoelectric effect. Using this theory, when sending an electric signal, the oscillator that consists on the two sides of the piezoceramics can bends and sends ultrasonic waves. Basing on the effect, we will use the piezoceramics in the ultrasonic sensor.
The piezoelectic materials
The piezoelectric effect occurs only in non conductive materials. Piezoelectric materials can be divided in two main groups: crystals and ceramics. The most well-known crystal piezoelectric materials is quartz (Sio2), and the ceramic piezoelectric materials is Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT). PZT is the best piezoceramics, but the pure PZT usually is not perfect, by doping the PZT material, its piezoelectric characteristics can be modified: especially the hardness or softness of the material, for example, doping the Sb2O3, Nb2O5, BaCO3 and so on.












